Clean Energy
Clean Energy Model
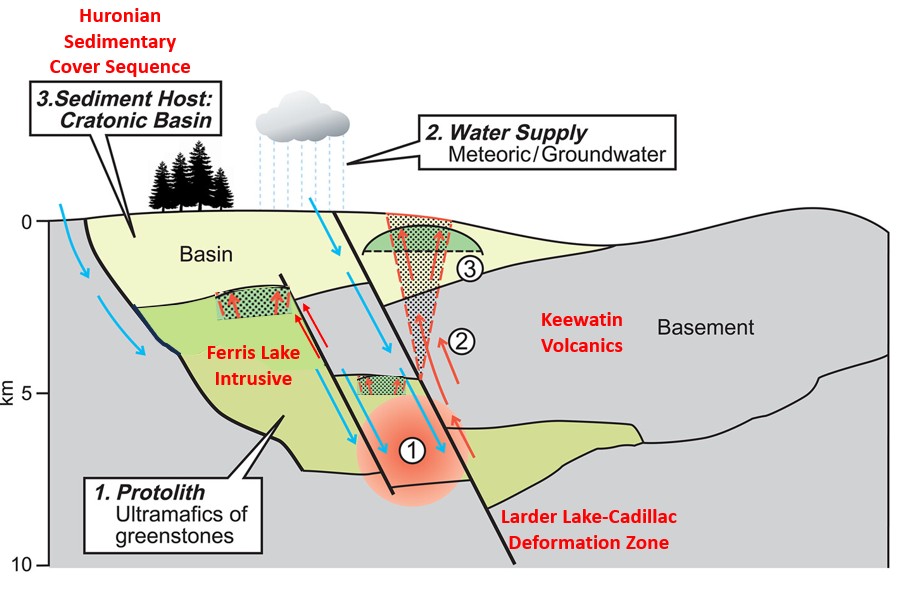
(Modified after: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP547-2023-39)
Cratonic greenstone exploration model. Depicts serpentinization of the Ferris Lake Intrusive protolith triggered by meteoric water supply and overlying Huronian Sedimentary Cover Sequence: (1) Zone of serpentinization reaction and hydrogen + helium generation; (2) Advection and solution flow of hydrogen and helium; (3) Sealing and trapping of gas-phase hydrogen and helium (modified from Hutchinson et al. 2024). Blue arrows: ground water; red arrows: hydrogen and helium.
•Clean energy is power generated with minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
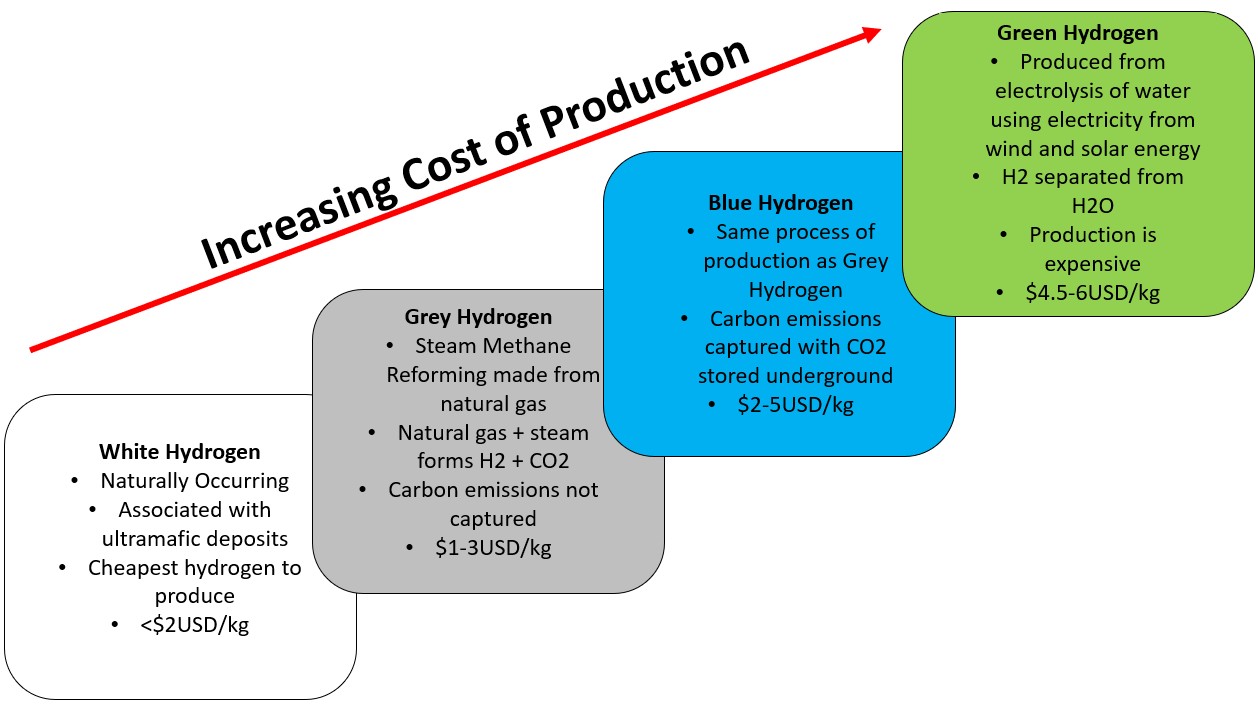
•Geological hydrogen (also known as natural, white, or gold hydrogen) is widely considered a promising clean energy source.
•Clean Burning: When used in a fuel cell or burned, it produces only water vapor and heat, with zero carbon dioxide emissions or other pollutants.
•Low-Carbon Extraction: Unlike most manufactured hydrogen (which uses fossil fuels and emits significant carbon dioxide), the extraction of geological hydrogen from naturally occurring underground reservoirs has a theoretically low or near-zero carbon footprint.
•Minimal Environmental Impact: The extraction process is expected to have a smaller ecological footprint and lower water consumption compared to traditional fossil fuel extraction or even green hydrogen production, which requires large amounts of water for electrolysis.
•Potential Renewability: Some researchers suggest that in certain active geological formations, hydrogen may be continuously generated, making it a potentially renewable resource.
•Helium is not an energy source in itself, but an indispensable, non-renewable natural resource that plays a vital supporting role in clean energy technologies.
•Essential for Green Tech: Helium is critical in the manufacturing of wind turbines and solar panels, and in the operation of nuclear fusion reactors (a potential future clean energy source), due to its unique properties as a non-toxic, inert, non-flammable gas with an extremely low boiling point.
•Non-Renewable Resource: On Earth, helium is a finite resource produced by the slow radioactive decay of uranium and thorium within the Earth's crust and mantle; It is also emitted from within olivine grains hosted in ultramafic intrusives as fluid inclusions or within the crystal lattice; once released into the atmosphere, it escapes into space.
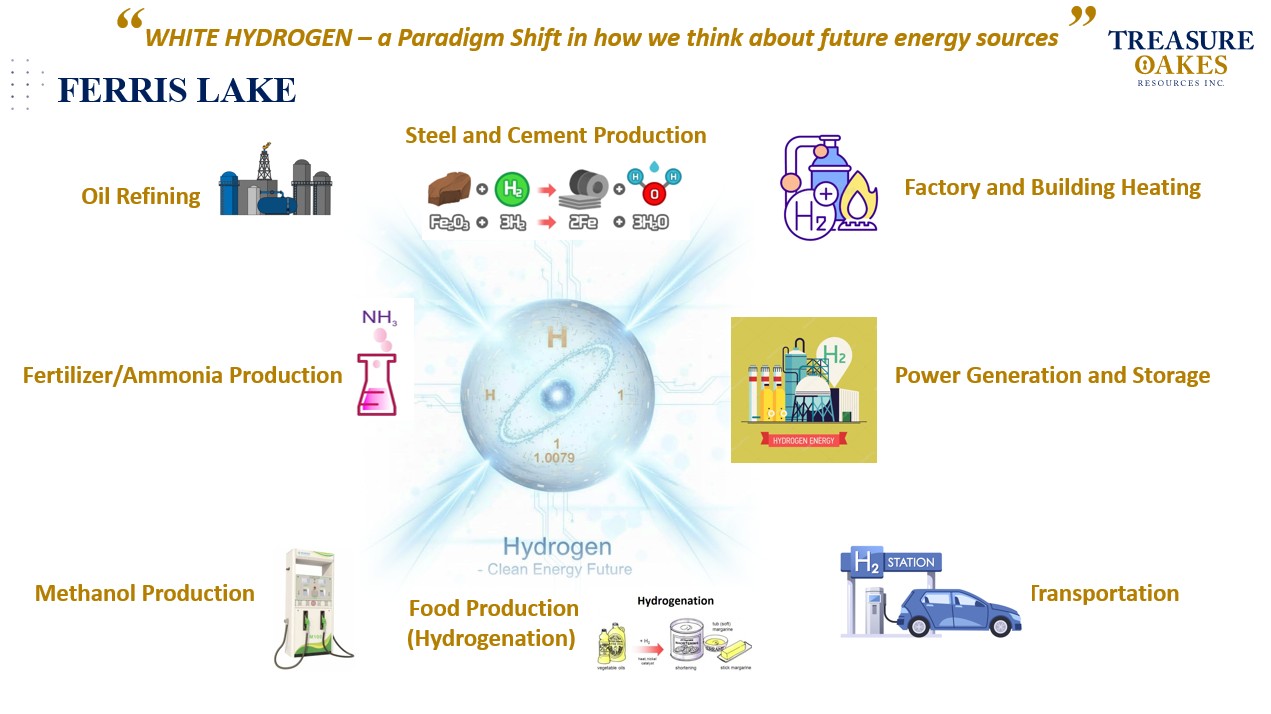
Clean Energy -Hydrogen

Clean Energy -Helium